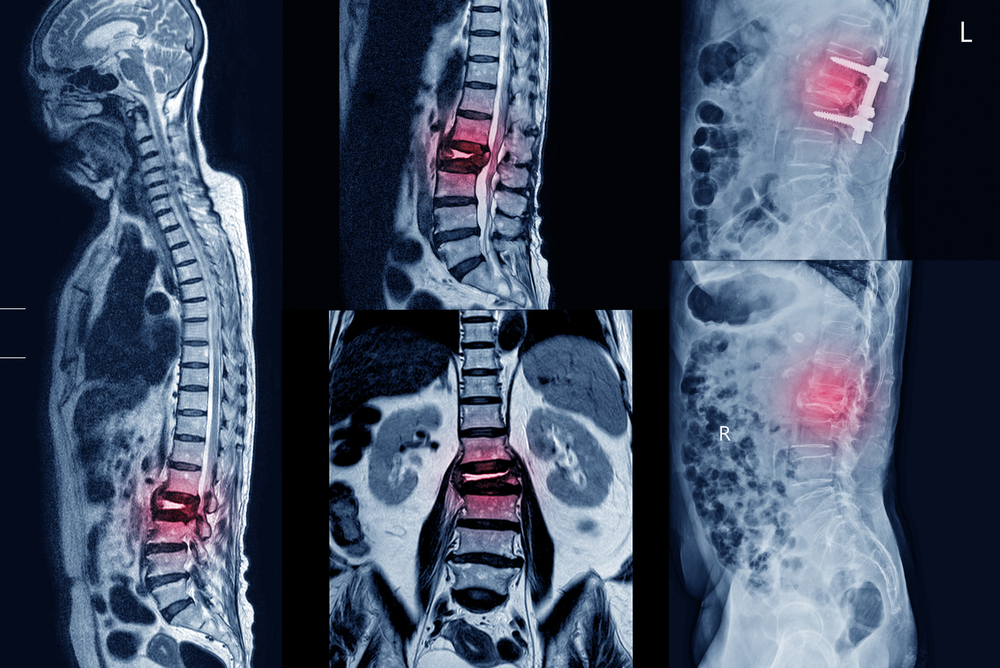
Thoracic Fusion

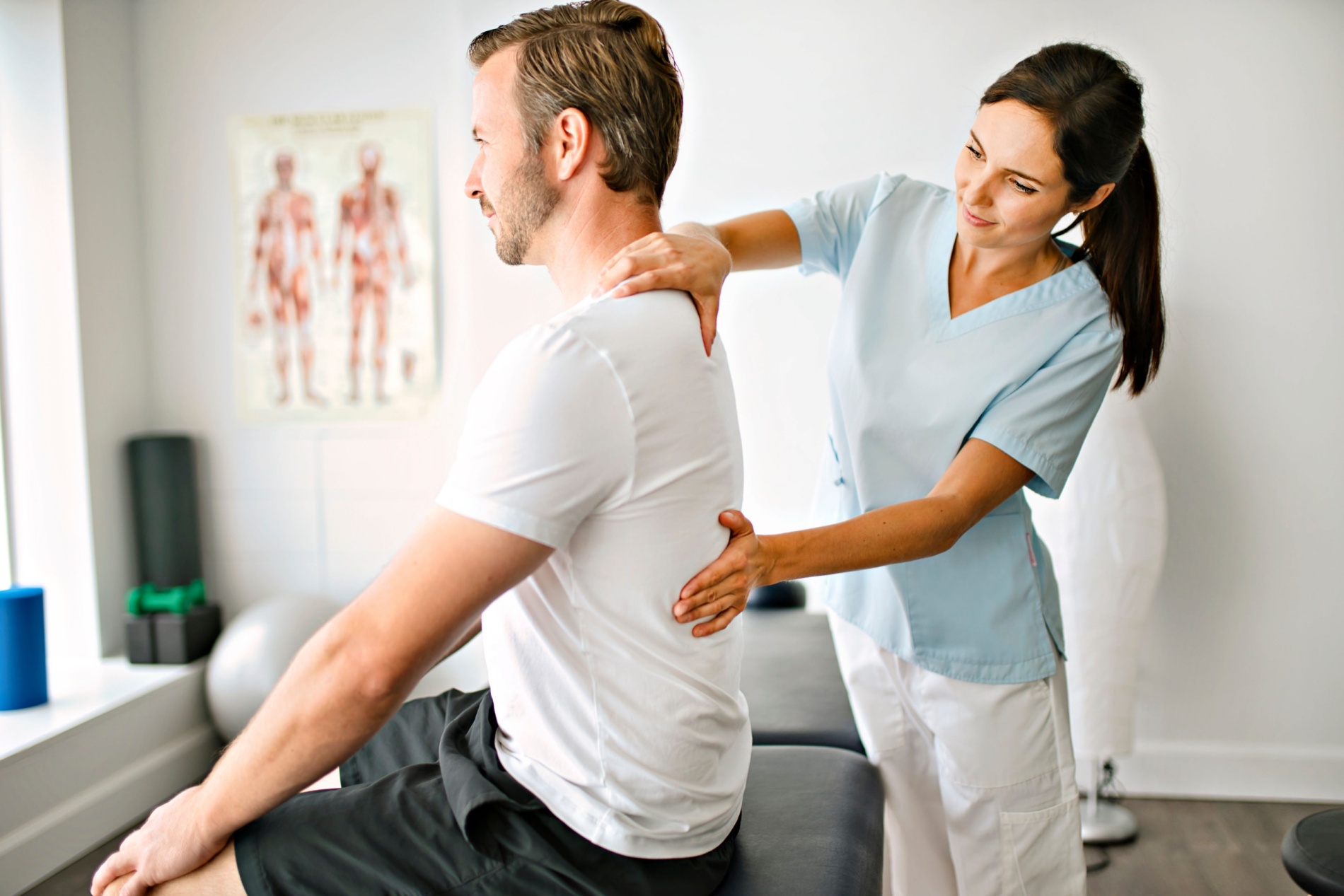
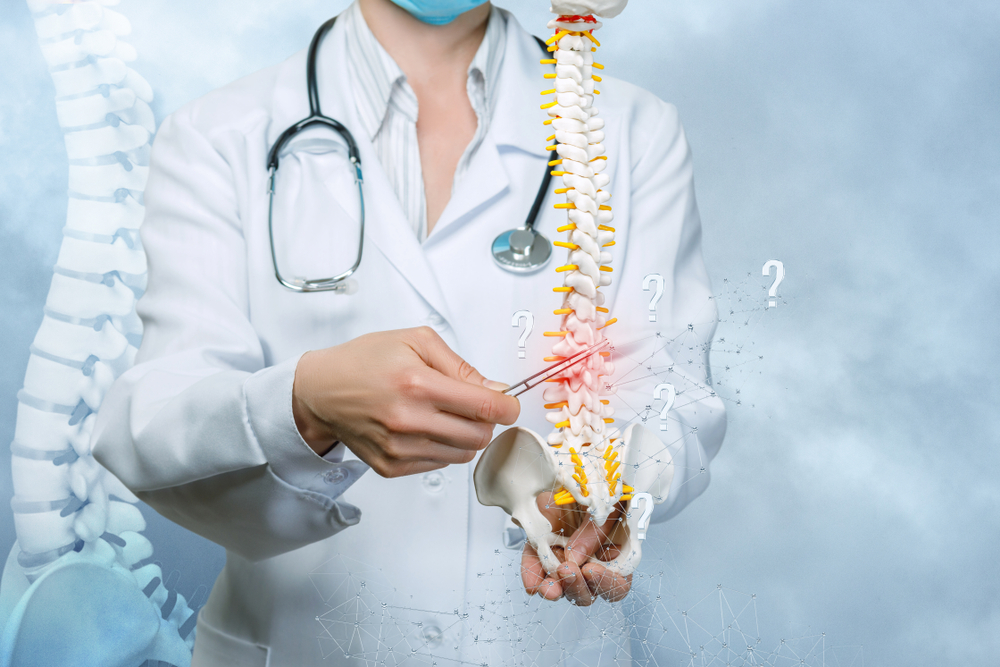
Thoracic fusion is a surgical procedure conducted on the thoracic spine, which is the middle portion of the vertebral column. This procedure is typically performed to address various spinal conditions, such as fractures, deformities, or instability in the thoracic region. During thoracic fusion, the surgeon makes an incision along the back, providing access to the thoracic spine.
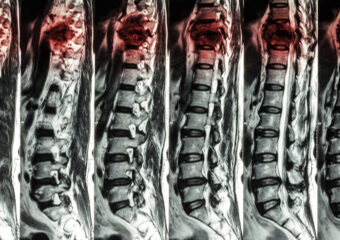
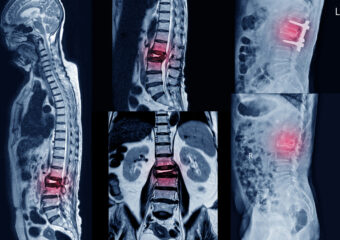

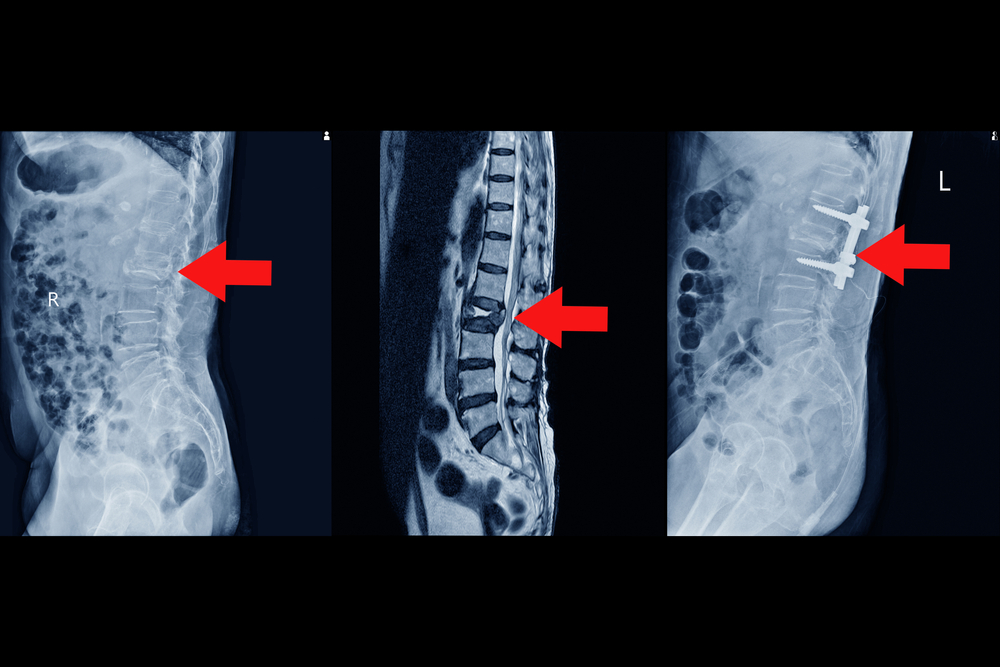
The specific approach may vary based on the nature of the spinal condition being treated. The procedure involves stabilizing the affected vertebrae using bone grafts, which may be taken from the patient’s own body (autograft) or obtained from a donor (allograft). Metal implants, such as rods, screws, or plates, are often used to secure the vertebrae in the desired alignment and facilitate the fusion process. Fusion is the gradual healing and joining of the vertebrae, creating a solid, stable segment of the spine.
A thoracic fusion is considered when conservative treatments have proven ineffective, and the goal is to restore stability, alleviate pain, and prevent further progression of the spinal condition. This procedure aims to create a solid fusion, reducing movement at the affected spinal segment and addressing symptoms associated with instability or deformity
Book An Appointment
"*" indicates required fields