Cervical Stenosis

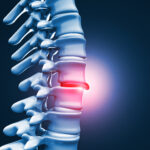
Cervical stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal in the neck region, known as the cervical spine. This narrowing can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots, leading to a variety of symptoms. Here’s an overview of cervical stenosis:
Causes of Cervical Stenosis:
- Degenerative Changes:
- The most common cause is the natural aging process, which can lead to wear and tear on the spinal discs and joints.
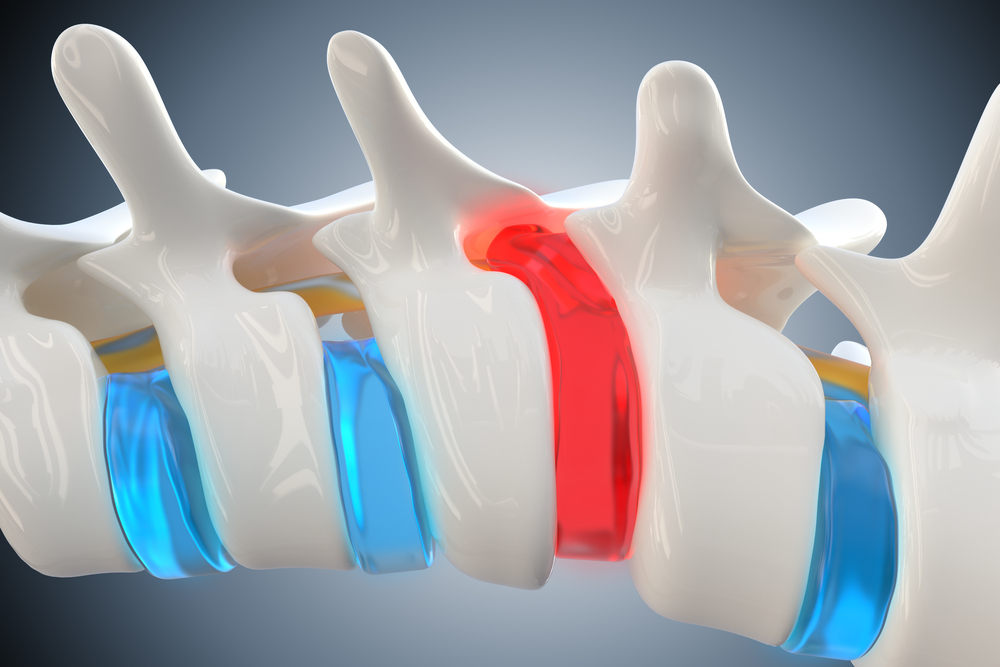
- Herniated Discs:
- Discs between the vertebrae may bulge or herniate, contributing to the narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Bone Spurs (Osteophytes):
- Over time, the formation of bone spurs can occur, limiting the space available for the spinal cord.
- Thickened Ligaments:
- Ligaments that support the spine may thicken over time, reducing the space within the spinal canal.
- Congenital Factors:
- Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to narrower spinal canals from birth.
- Trauma or Injuries:
- Accidents or injuries to the neck can lead to inflammation and contribute to cervical stenosis.
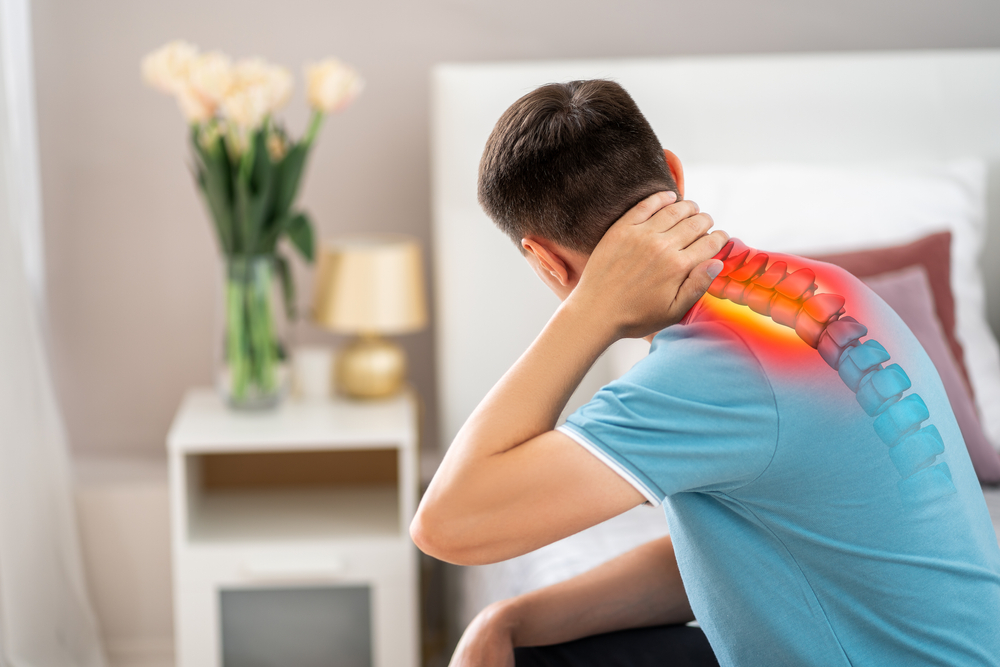
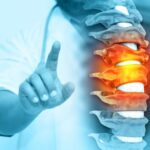
Symptoms of Cervical Stenosis:
- Neck Pain:
- Persistent or intermittent pain in the neck.
- Radiating Pain:
- Pain may radiate into the shoulders, arms, or hands.
- Numbness/Tingling:
- Sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities.
- Weakness:
- Muscle weakness, particularly in the arms or hands.
- Coordination Issues:
- Difficulty with balance and coordination.
- Difficulty Walking:
- Severe cases may lead to difficulty walking or loss of bladder/bowel control (rare).
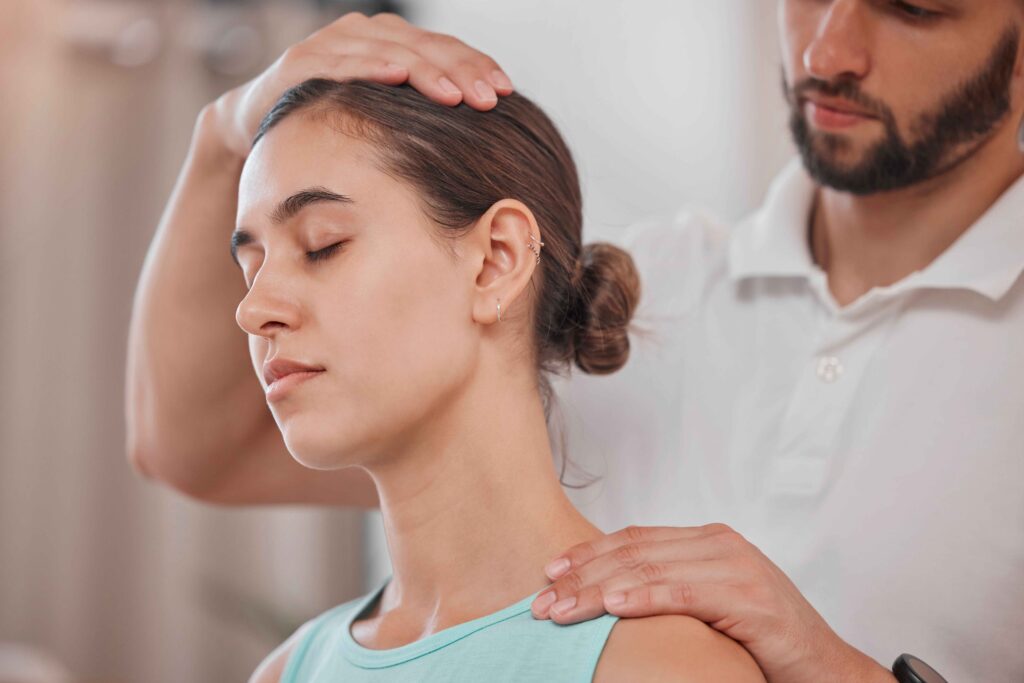
Diagnosis and Evaluation
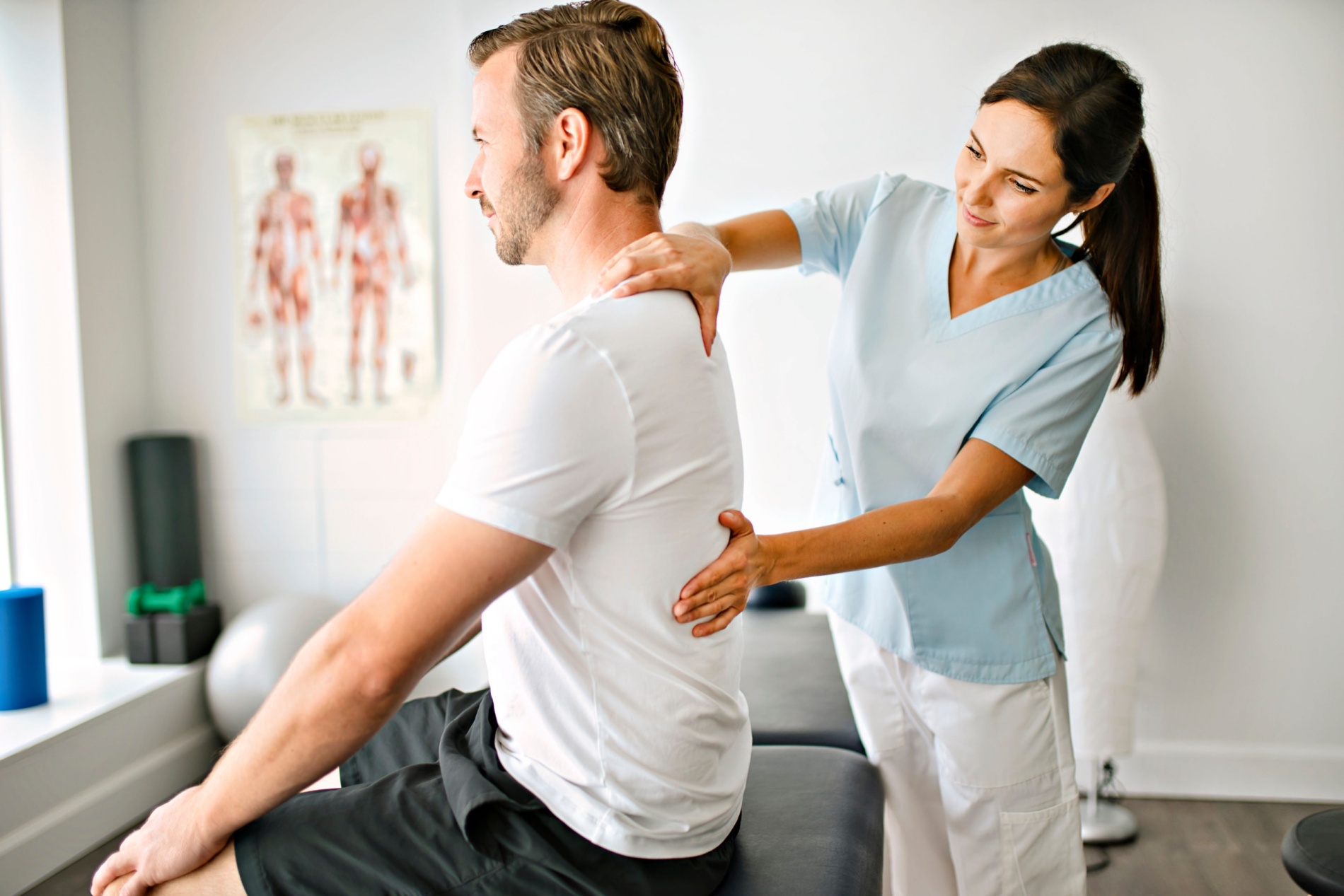
- Physical Examination:
- A healthcare professional may conduct a thorough examination to assess symptoms, range of motion, and neurological function.
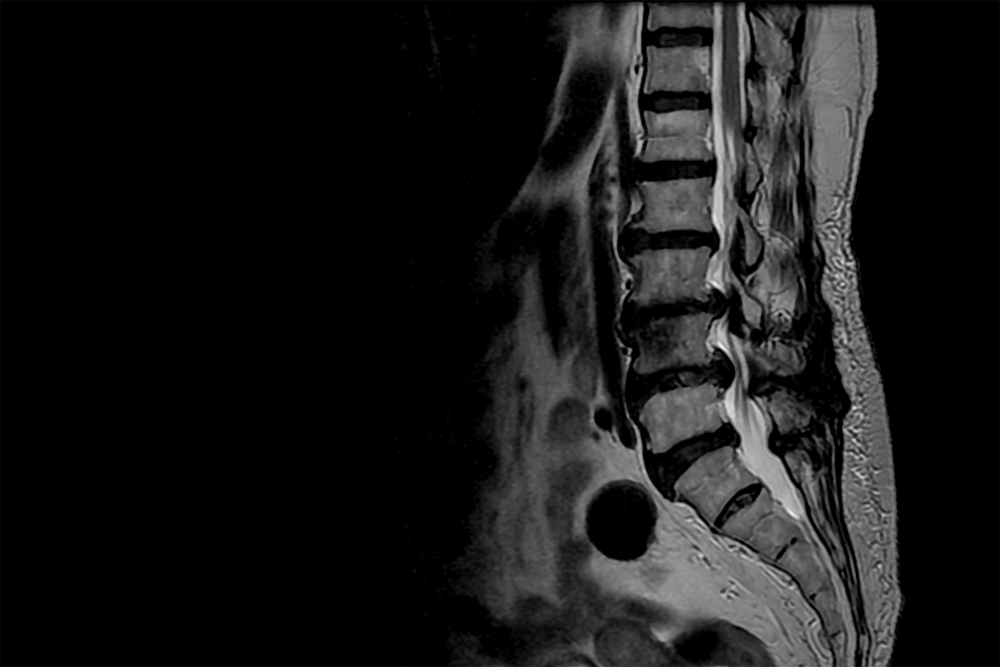
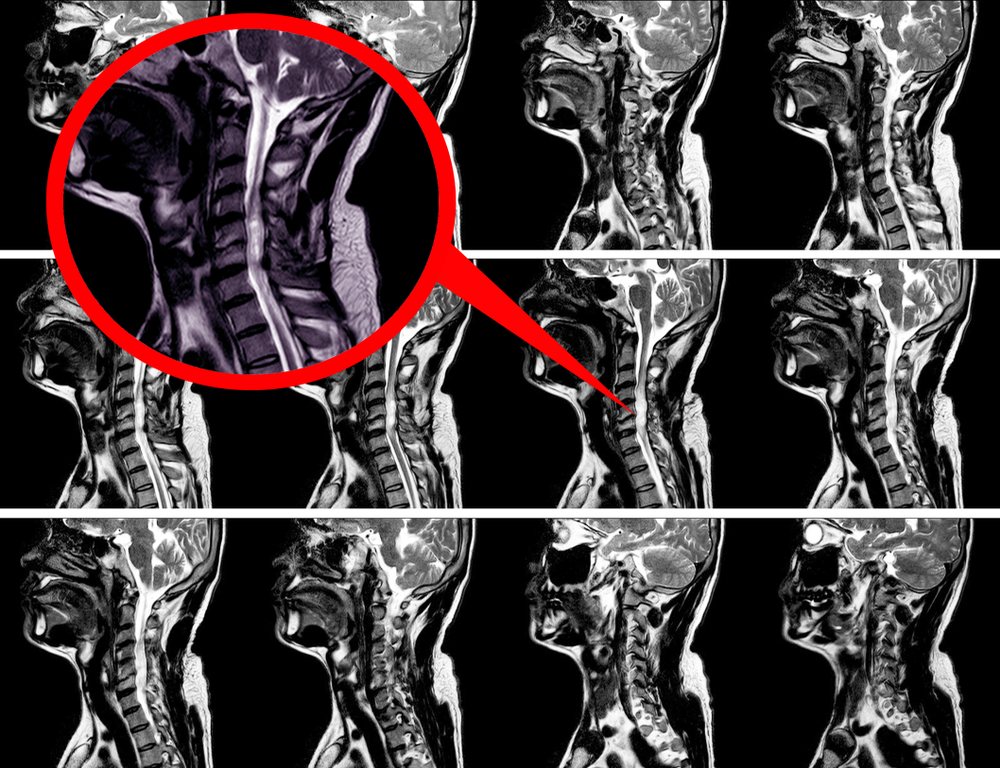
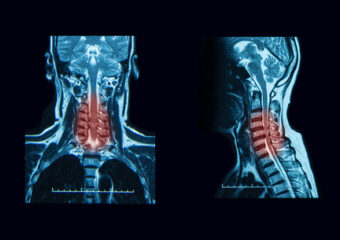
- Imaging Studies:
- MRI or CT scans can provide detailed images of the cervical spine, helping to identify the extent of stenosis and any associated abnormalities.
- Electromyography (EMG):
- EMG may be used to evaluate nerve function and identify areas of compression.
Treatment Options:
- Conservative Measures:
- Rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques may be recommended initially.
- Medications:
- Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants can help manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy:
- Specific exercises can improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and alleviate pressure on the spinal cord.
- Epidural Steroid Injections:
- In some cases, injections of steroids into the epidural space may help reduce inflammation and provide relief.
- Surgical Intervention:
- For severe cases or when conservative measures are ineffective, surgery may be considered. Procedures such as laminectomy or spinal fusion may be performed to decompress the spinal canal.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and individual patient factors. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most appropriate course of action for cervical stenosis

Book an appointment
"*" indicates required fields