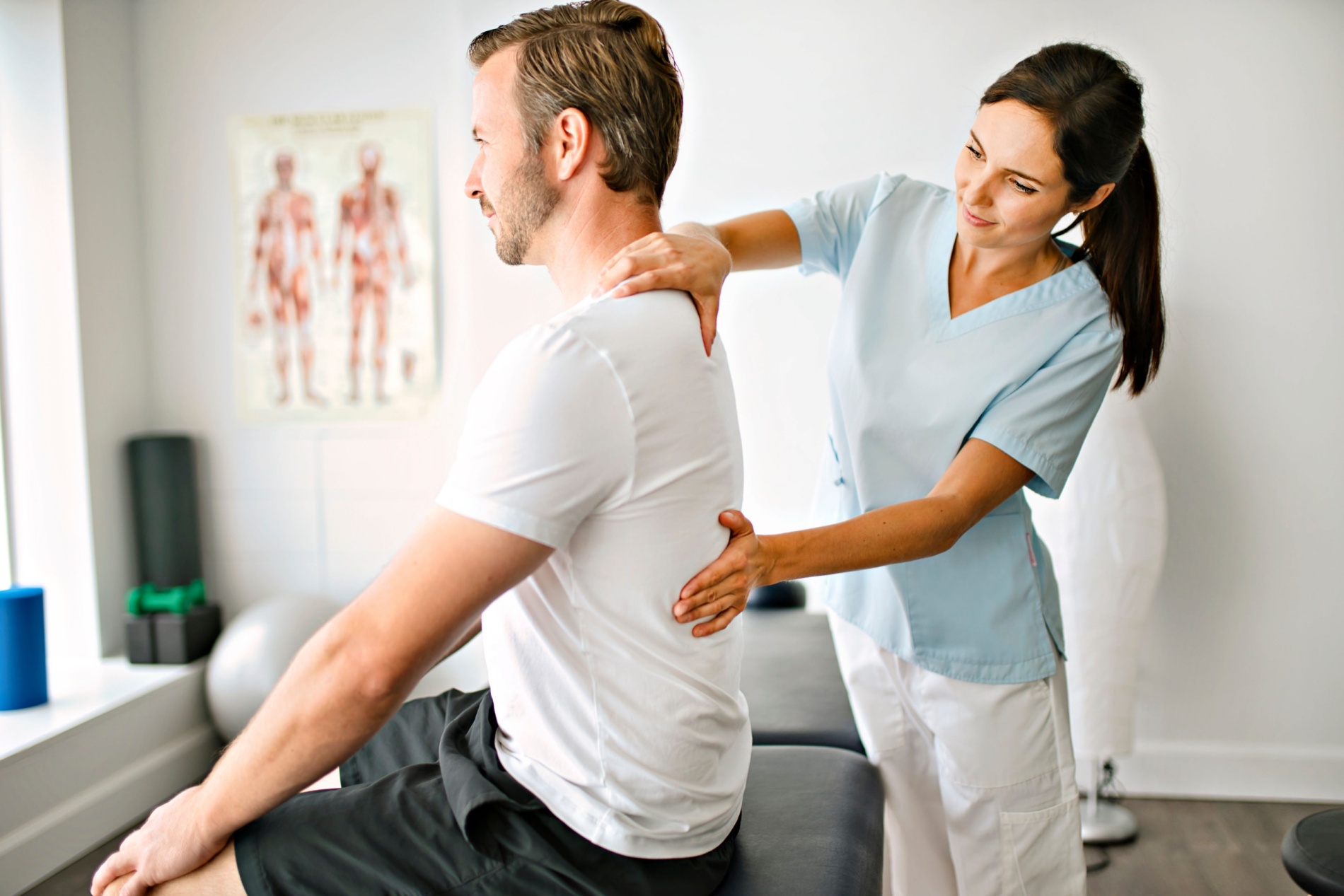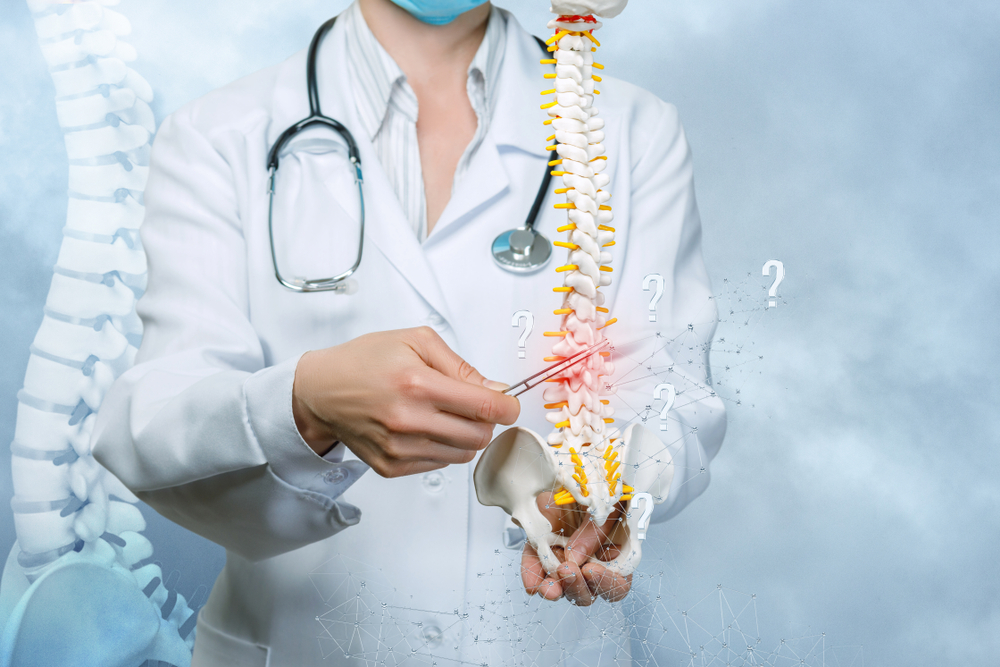
Thoracic Spondylosis

Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition that affects the thoracic spine, which is the middle portion of the spine consisting of 12 vertebrae (T1 to T12). Spondylosis is a term that generally refers to age-related wear and tear on the spine, and it can manifest in various regions, including the thoracic spine.

In thoracic spondylosis, degenerative changes such as the development of osteophytes (bone spurs), loss of disc height, and changes in the facet joints may occur. These changes can contribute to symptoms like mid-back pain, stiffness, and decreased flexibility. The thoracic spine is less commonly affected by spondylosis compared to the lumbar (lower back) or cervical (neck) spine.
Common causes of thoracic spondylosis include the natural aging process, repetitive stress on the spine, poor posture, and genetic factors. As the intervertebral discs and facet joints in the thoracic spine undergo degenerative changes, they can lead to discomfort and reduced mobility. Symptoms of thoracic spondylosis may include aching or stiffness in the mid-back, limited range of motion, and, in some cases, radiating pain to the chest or abdomen. Severe cases may result in compression of nerve roots, leading to neurological symptoms
Book an appointment
"*" indicates required fields