SI Joint Dysfunction

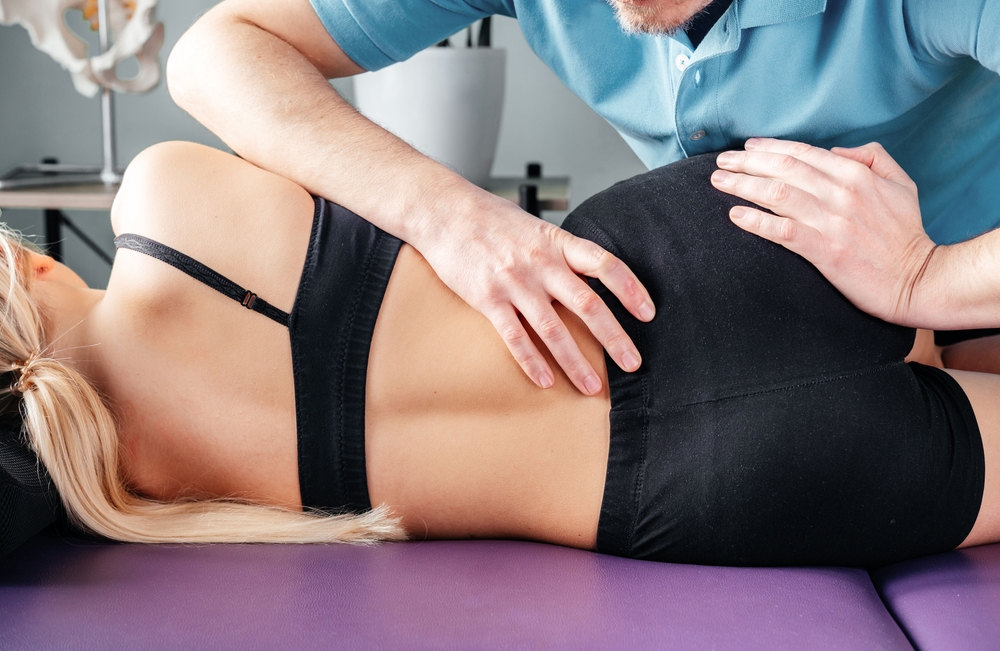
The sacroiliac (SI) joints are located where the sacrum (the triangular bone at the base of the spine) meets the iliac bones (the large pelvic bones). These joints play a crucial role in transferring forces between the upper body and the legs. Dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint, often referred to as SI joint dysfunction or SI joint pain, occurs when there is an abnormality in the function of these joints. SI joint dysfunction can manifest as pain and discomfort in the lower back, buttocks, and sometimes the legs. The pain may be sharp or dull, and it can be exacerbated by activities such as standing, sitting, walking, or climbing stairs. The exact cause of SI joint dysfunction can vary, but common factors include trauma or injury, pregnancy and childbirth, arthritis, or degenerative changes in the joint over time.
Diagnosing SI joint dysfunction can be challenging because the symptoms can overlap with other conditions affecting the spine and hips. Healthcare professionals often use a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging (such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans) to assess and diagnose SI joint dysfunction.
Treatment for SI joint dysfunction may involve a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, more invasive interventions. Conservative approaches include physical therapy, exercises to stabilize the joint, medications for pain and inflammation, and the use of braces or belts to support the SI joint. In more severe cases, injections of corticosteroids or other medications into the joint may be considered. In rare instances, surgery may be recommended
Book an appointment
"*" indicates required fields