Myelopathy

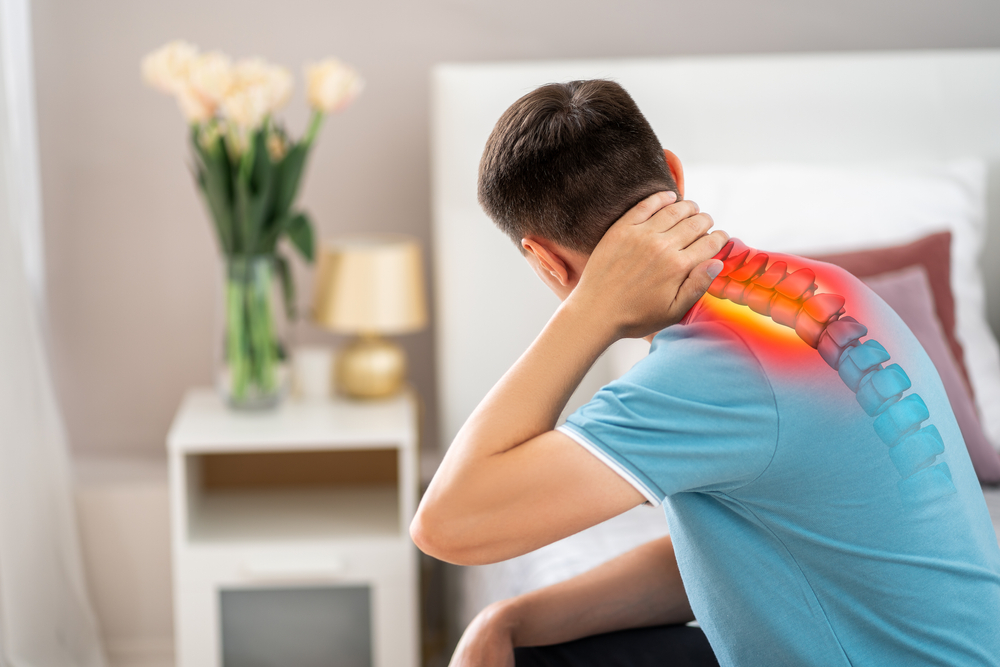
Cervical myelopathy is a condition characterized by dysfunction of the spinal cord in the neck region, specifically in the cervical spine. It is often caused by compression or narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. Here’s an overview:
Causes of Cervical Myelopathy:
- Degenerative Changes:
- The most common cause is the natural aging process, resulting in wear and tear on the spinal discs, joints, and ligaments.
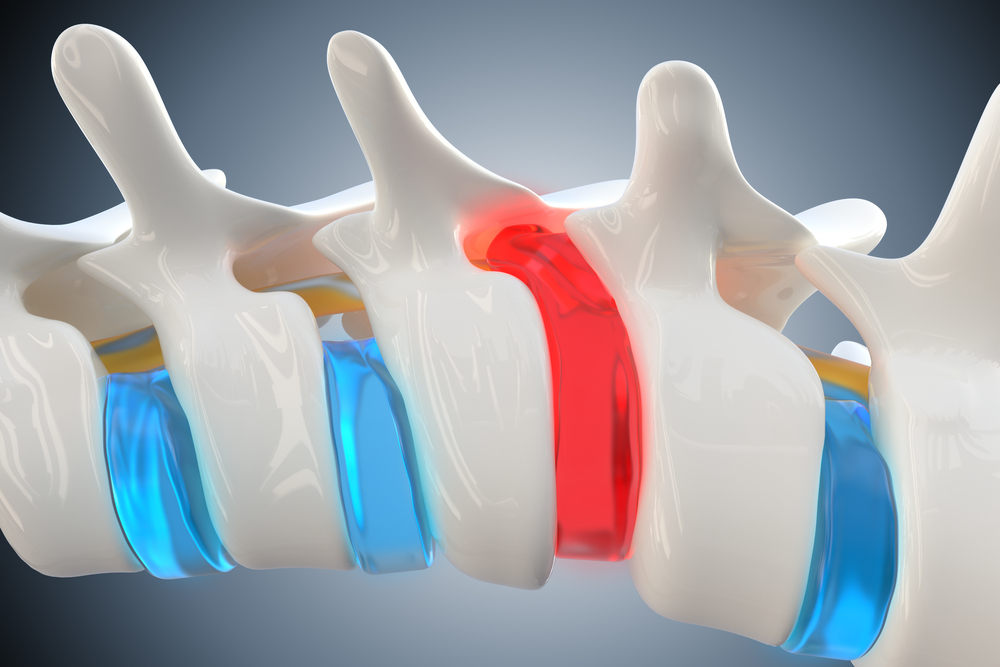
- Herniated Discs:
- Discs between the vertebrae may herniate, pressing on the spinal cord.
- Spinal Stenosis:
- Narrowing of the spinal canal can occur due to factors such as bone spurs, thickened ligaments, or disc degeneration.
- Trauma or Injuries:
- Accidents or injuries to the neck can lead to compression of the spinal cord.
- Tumors:
- Abnormal growths in or around the spinal cord may contribute to compression.
Symptoms of Cervical Myelopathy:
- Gait Disturbances:
- Difficulty walking or changes in coordination.
- Hand Coordination Issues:
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, such as writing or buttoning clothes.
- Weakness:
- Muscle weakness, particularly in the hands and arms.
- Numbness/Tingling:
- Sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities.
- Neck Pain:
- Pain or discomfort in the neck, though this may not always be present.
- Loss of Bladder/Bowel Control (Rare):
- In severe cases, there may be loss of bladder or bowel control.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- A healthcare professional will gather information about symptoms and conduct a physical examination to assess neurological function.
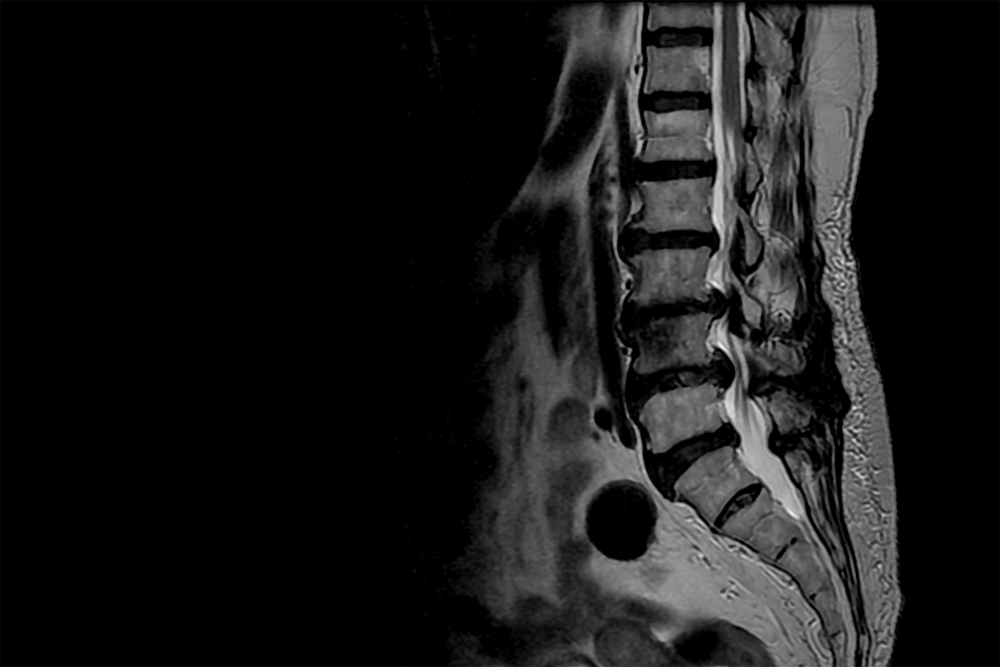
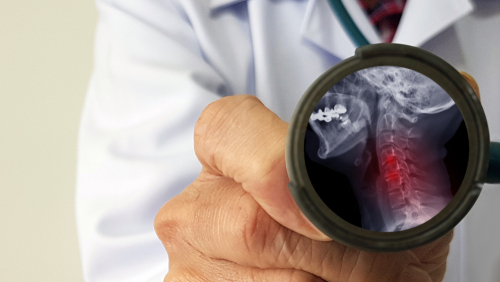
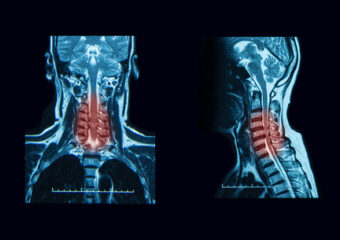
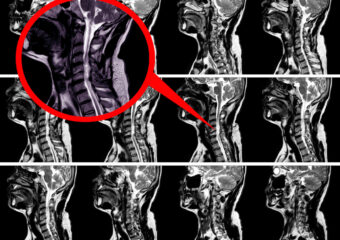
- Imaging Studies:
- MRI or CT scans can provide detailed images of the cervical spine, helping to identify the extent of compression and any contributing factors.
- Electromyography (EMG):
- EMG may be used to evaluate nerve and muscle function.
Treatment Options:
- Conservative Measures:
- Initial treatment may include rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques.
- Medications:
- Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy:
- Specific exercises can improve strength, flexibility, and overall function.
- Bracing:
- In some cases, wearing a cervical collar or brace may be recommended to limit neck motion and reduce strain on the spinal cord.
- Surgical Intervention:
- For severe cases or when conservative measures are ineffective, surgery may be considered. Procedures such as decompression surgery (e.g., laminectomy) or spinal fusion may be performed.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and individual patient factors. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most appropriate course of action for cervical myelopathy. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent further neurological deterioration
Book an appointment
"*" indicates required fields